How to Convert Fractions to Decimals A Simple Guide
Learn how to convert fractions to decimals with our simple guide. Master long division, shortcuts, and common examples to boost your math skills.

The simplest way to convert a fraction to a decimal is to just divide the top number (the numerator) by the bottom number (the denominator). That little fraction bar actually means "divide by." This one simple action works for any fraction you can think of, from 1/2 to 17/32.
Why Converting Fractions to Decimals Is a Crucial Skill
Ever find yourself in a store, staring at two signs—one says "1/3 off" and the other says "25% off"—and your brain freezes for a second? That’s the real world asking you to convert a fraction. This isn't just a textbook problem; it's a practical skill that helps you make sense of the numbers all around you.
At its heart, every fraction is just a division problem in disguise. Once you get that, a lot of math starts to feel less intimidating and more intuitive. It's a fundamental concept that shows up in some pretty unexpected places:
- In the kitchen: Your recipe calls for 3/4 of a cup, but the digital scale you're using only shows decimals.
- In the workshop: You need a 5/8-inch drill bit. Knowing its decimal equivalent, 0.625, helps you grab the right one from a set measured in decimals.
- In finance: A stock might go up 1/4 of a point. That means it increased by $0.25.
Building a Strong Mathematical Foundation
Getting this conversion down isn't just about memorizing steps. It's about really understanding how different forms of numbers relate to each other. Studies have shown that a solid grasp of fractions is a major predictor of success in more advanced math, like algebra. In fact, when students get stuck in algebra, the problem can often be traced back to a shaky foundation with fractions.
By learning how to convert fractions to decimals, you aren’t just learning a procedure. You are developing number sense—the intuitive ability to understand, relate, and work with numbers flexibly.
This skill makes comparing values a whole lot easier. Which is bigger, 7/16 or 3/8? It’s tough to tell at a glance. But once you convert them to 0.4375 and 0.375, the answer is obvious. This kind of clarity is vital for everything from analyzing data to acing standardized tests.
If you're looking to build up your core math abilities, it's worth understanding the importance of GCSE Maths and how it sets you up for future success.
Ultimately, knowing how to switch between fractions and decimals gives you the confidence to handle a data-driven world. For more tips on building these essential skills, take a look at our guide on how to study math effectively.
The Universal Method: Using Long Division
When you come across a fraction that you can't easily simplify, long division is your go-to, failsafe method. Think of it as the universal key that works on any fraction, no matter how awkward it looks. The core concept is refreshingly simple: every fraction is just a division problem in disguise. The fraction 3/4, for example, literally means 3 divided by 4.
To get started, you'll set up a standard long division problem. The numerator (the top number) goes inside the division bracket—it’s your dividend. The denominator (the bottom number) sits outside as the divisor.
Let's walk through converting 3/4 to a decimal this way. You'd place the 3 inside the bracket and the 4 outside. Right away, you hit a snag: 4 doesn't go into 3. This is where the process really begins. Just add a decimal point and a zero after the 3, turning it into 3.0. Don't forget to put a decimal point directly above in your answer area to keep everything perfectly aligned.
Working Through an Example
Now, you can treat 3.0 as 30. How many times does 4 go into 30? It fits 7 times (4 x 7 = 28). You'll write the 7 right after the decimal in your answer.
Next, subtract 28 from 30, which leaves a remainder of 2. Since we're not at zero yet, we keep going. Add another zero to the dividend and bring it down, turning that 2 into a 20. How many times does 4 go into 20? It goes in exactly 5 times (4 x 5 = 20).
You pop that 5 into your answer, subtract 20 from 20, and you're left with a remainder of 0. Hitting a zero remainder means you're done! The number you've built in the answer area, 0.75, is the decimal form of 3/4.
This simple visual shows how a fraction transforms into its decimal counterpart.
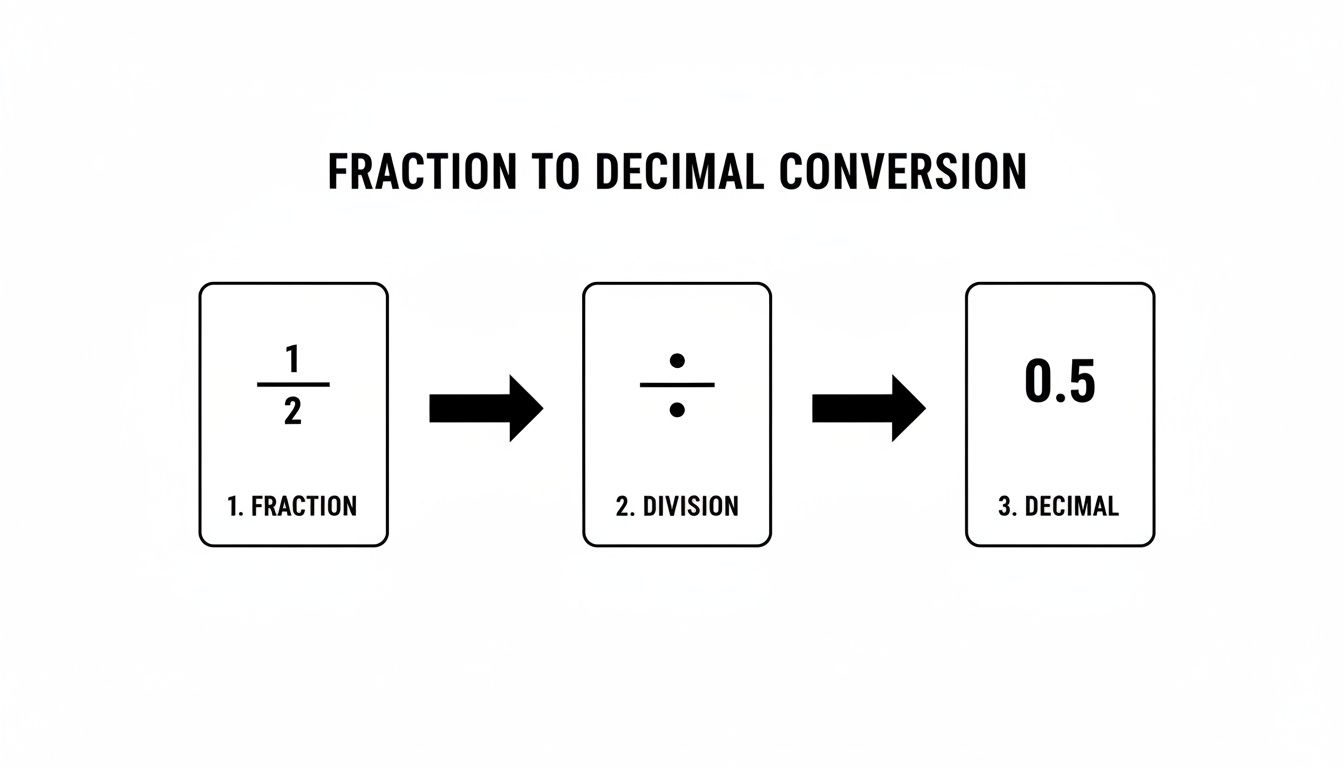
The infographic perfectly illustrates that the division symbol acts as the bridge between these two ways of writing the same value.
Tackling a More Complex Fraction
Ready for something a bit trickier? Let's convert 5/8. The setup is the same: 5 goes inside the bracket, 8 goes outside. And just like before, 8 doesn't go into 5, so we add a decimal and a zero to make it 5.0.
Here's the breakdown:
- 8 goes into 50 six times (8 × 6 = 48), leaving a remainder of 2.
- Bring down a zero to make it 20. 8 goes into 20 two times (8 × 2 = 16), leaving a remainder of 4.
- Bring down another zero, making it 40. 8 goes into 40 exactly five times (8 × 5 = 40), leaving a remainder of 0.
And there's our answer: 0.625. This methodical process is what makes long division so reliable. For a deeper dive into problem-solving techniques, check out our guide on how to solve math problems step by step.
The best part about long division is its consistency. It doesn't matter if the fraction is simple or complex; the rules are always the same. Adding zeros and carrying down remainders will always guide you straight to the correct decimal.
This method has deep roots. In 1585, Simon Stevin's work on decimal fractions was a game-changer for European commerce. But even today, doing it by hand can take time. One study found that 62% of high school students take over two minutes to manually convert a fraction like 5/16. Still, learning long division is a fundamental skill that helps you truly understand the "why" behind the conversion, not just the answer a calculator spits out.
A Smarter Way: Simplifying Fractions Before You Convert
Sure, long division always works, but it’s not always the fastest route. When it comes to math, working smarter often means finding a shortcut, and simplifying a fraction first is one of the best I know. Taking a moment to check for this can save you a surprising amount of work.
Simplifying is all about finding the greatest common factor (GCF). That’s just a fancy term for the biggest number that divides evenly into both your numerator and denominator. Once you find it, you divide both parts of the fraction by that number. This shrinks the numbers you have to deal with but keeps the fraction's value exactly the same.
Let's look at 12/16. The thought of dividing 12 by 16 might make you groan. But wait. Both numbers are clearly divisible by 4.
- 12 divided by 4 is 3.
- 16 divided by 4 is 4.
Just like that, 12/16 becomes the much friendlier 3/4. Now, the division problem (3 ÷ 4) is a breeze, giving you 0.75. You get the same answer you would have gotten from 12 ÷ 16, but with way less hassle.
This kind of thinking is a game-changer, especially for younger students. Getting comfortable with manipulating fractions is a cornerstone for later success in algebra. If you're looking for more ways to build these skills, these math problems for 5th graders are a great resource.
The Power of Ten Method
Here's another great trick that avoids long division entirely: the "power of ten" method. This is perfect for fractions where the denominator can be easily multiplied to become 10, 100, 1000, and so on. If you see a denominator like 2, 4, 5, 20, 25, or 50, your brain should light up.
The idea is to create an equivalent fraction that has a power of ten as its denominator. Take the fraction 4/5. To get the denominator (5) to become 10, you just multiply it by 2. But to keep the fraction's value the same, you have to do the exact same thing to the numerator (4).
- Numerator: 4 × 2 = 8
- Denominator: 5 × 2 = 10
Your new fraction is 8/10. Now, the conversion is practically done for you. The fraction 8/10 literally means "eight-tenths," which as a decimal is written as 0.8. No division required.
This method is fantastic because it directly links the idea of a fraction to decimal place values. When you turn a fraction like 13/25 into 52/100, you're actually seeing the decimal 0.52 take shape right in front of you.
Let's try 3/4. I know I can turn a 4 into 100 by multiplying it by 25. So, I'll do that to both the top and bottom.
- Multiply the numerator: 3 × 25 = 75
- Multiply the denominator: 4 × 25 = 100
The equivalent fraction is 75/100, which is simply 0.75.
Once you start spotting these opportunities, you'll be able to convert many common fractions to decimals in your head, sharpening your mental math and saving tons of time.
To help you get faster at this, here's a quick reference table for some common denominators.
Common Fraction Denominators and Their Decimal Equivalents
| Original Denominator | Multiply By | New Denominator | Example Fraction | Decimal Conversion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 5 | 10 | 1/2 → 5/10 | 0.5 |
| 4 | 25 | 100 | 3/4 → 75/100 | 0.75 |
| 5 | 2 | 10 | 4/5 → 8/10 | 0.8 |
| 8 | 125 | 1000 | 5/8 → 625/1000 | 0.625 |
| 20 | 5 | 100 | 7/20 → 35/100 | 0.35 |
| 25 | 4 | 100 | 11/25 → 44/100 | 0.44 |
| 50 | 2 | 100 | 17/50 → 34/100 | 0.34 |
Getting familiar with these common conversions will make you much quicker and more confident when working with fractions and decimals.
Dealing with Mixed Numbers and Repeating Decimals
Not every fraction fits neatly into the basic methods. You'll run into special cases like mixed numbers and decimals that seem to go on forever. But don't let them throw you off. The logic for handling them is straightforward once you know the tricks.
How to Handle Mixed Numbers
A mixed number like 3 ½ is just a whole number and a fraction hanging out together. The simplest way to convert it is to handle them separately.
First, just ignore the whole number (3) for a second and focus on the fraction (½). We know that ½ is 0.5. Now, just bring that whole number back into the picture and add it to the decimal.
So, 3 + 0.5 = 3.5. That’s it! This little trick saves you from having to convert the mixed number into a messy improper fraction first.
What About Repeating Decimals?
Okay, so what happens when a fraction doesn't convert into a nice, clean decimal? Take a fraction like 2/3. If you start doing the long division, you'll see a pattern emerge pretty quickly. You divide 2 by 3, get a remainder of 2, bring down a zero, and end up dividing 20 by 3 again and again.
This creates a decimal that never ends: 0.666.... We call this a repeating decimal.

To avoid writing out an endless string of sixes, we use a shorthand called bar notation. Just place a bar over the digit (or digits) that repeat.
For 0.666..., you’d simply write 0.6̅.
Here are a few other common examples you'll likely come across:
- 1/3 turns into 0.3̅
- 1/6 becomes 0.16̅ (notice the bar is only over the 6, since the 1 doesn't repeat)
- 5/11 becomes 0.45̅ (here, the pattern "45" repeats)
Why Do Some Fractions Repeat Anyway?
The secret to whether a decimal will terminate or repeat lies in the fraction's denominator. After you've simplified the fraction, look at the prime factors of the denominator. If the only prime factors are 2s and 5s, the decimal will terminate. For instance, the denominator in 3/8 is 8, which is 2x2x2. It only has 2s, so it gives you a clean 0.375.
But if the denominator has any other prime factor (like 3, 7, 11, etc.), you're guaranteed to get a repeating decimal. That’s precisely why 2/3 repeats—its denominator is the prime number 3.
A Bit of History: The idea of decimals has been around for centuries. Francesco Pellos first used a decimal point back in 1492, but it was mathematicians like Euler who later helped formalize our understanding of these eternally repeating numbers.
It's no surprise that many students get tripped up here. In the U.S., national test data shows that roughly 68% of 8th graders find fraction-to-decimal conversions challenging. If you're curious, you can learn more about the historical development of fractions and decimals and how they shaped modern math.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
It’s a great feeling when converting fractions to decimals finally clicks, but even the sharpest students can run into a few common snags. Tiny missteps can derail your work, especially when you're deep in a long division problem. Knowing what these tripwires are is the best way to sidestep them and really master the skill.
One of the most common mistakes I see is flipping the fraction when setting up the division. It’s so easy to accidentally divide the denominator by the numerator—for example, trying to solve 4 ÷ 3 for the fraction 3/4. Just remember this golden rule: the top number (numerator) always goes inside the division box.
Another frequent hiccup is misplacing the decimal point. As soon as you add a decimal and a zero to the number inside the box (like turning 3 into 3.0), you have to pop a decimal point straight up into your answer line. If you forget this, your entire answer will be off.
Rounding and Relying on Calculators
Things can also get a little fuzzy with rounding repeating decimals. Take 2/3, which comes out to 0.666... It's tempting to just round that up to 0.67. While that’s sometimes what a problem asks for, it's crucial to understand why you're rounding. If the instructions don't say to round, the most precise way to write your answer is with bar notation (0.6̅) to show the repeating digit.
A calculator is fantastic for double-checking your answers, but leaning on it too heavily can keep you from really getting the hang of the process. Try to use it to confirm your work, not to do the work. This helps you build a much stronger feel for how numbers work together.
This isn't just a classroom issue; it has real-world implications. A PISA survey across 80 countries found that only 42% of 15-year-olds could correctly convert 3/8 to 0.375 under pressure. That kind of skill gap can even affect economic productivity. As you can see from the history of fractions on nrich.maths.org, even with centuries of practice, these small errors are still common, which shows just how important it is to get the fundamentals right.
Here are a few quick tips to help you stay accurate:
- Check the Setup: Before you do any math, glance back and confirm the numerator is inside the division box.
- Decimal Point First: Place the decimal in your answer as soon as you add one to the number you're dividing.
- Keep It Tidy: Lined paper is your friend! Keeping your columns straight makes it much easier to track your work as you bring down zeros.
Paying attention to these little details will save you a lot of frustration and help you turn fractions into decimals with confidence.
Got More Questions About Fractions?
Even after you get the hang of the main methods, a few specific questions tend to trip people up. Nailing down these details will really cement your understanding and give you the confidence to tackle any problem that comes your way. Let's walk through some of the most common ones.
What's the Fastest Way to Convert a Fraction Without a Calculator?
For a quick mental conversion, nothing beats the "power of ten" trick. This little shortcut works like a charm whenever the fraction's denominator is a number that plays nicely with 100—think 2, 4, 5, 20, or 25.
The idea is to find a number you can multiply the denominator by to turn it into 10, 100, or 1000. Take 3/25, for instance. You know that 25 x 4 = 100. So, just multiply the top and bottom by 4 to get 12/100. Right away, you know the answer is 0.12. No long division required!
This mental math shortcut is so effective because it connects the fraction directly to the decimal place value system. Learning to spot these opportunities is a huge step toward building better number sense and speed.
How Do I Know if the Decimal Will End or Repeat?
Believe it or not, you can tell just by looking at the fraction's denominator. The secret lies in its prime factors, but only after the fraction is simplified as much as possible.
Here’s the rule of thumb:
- It will be a terminating (ending) decimal if... the denominator’s prime factors are only 2s and 5s. For example, in the fraction 7/20, the denominator is 20. Its prime factors are 2 x 2 x 5. Since there are only 2s and 5s, the decimal has to end, which it does: 0.35.
- It will be a repeating decimal if... the denominator has any other prime factor in the mix (like 3, 7, 11, and so on). That's precisely why 1/3 becomes 0.333...—its denominator is the prime number 3.
This is a fantastic trick for double-checking your answers and really understanding why some fractions produce those endless repeating patterns.
Does This Still Work for Improper Fractions?
Yep, it absolutely does. The method for converting an improper fraction (where the top number is bigger than the bottom) is exactly the same. You just divide the numerator by the denominator.
The only real difference is what the answer looks like. Since an improper fraction is always worth more than one, its decimal form will always be a number greater than 1.0. If you convert 7/4, you're just dividing 7 by 4. The result? 1.75. Simple as that.
What Should I Tackle Next?
Once you're comfortable turning fractions into decimals, it's a great idea to explore the other conversions. Building these connections helps you see the bigger picture of how different numbers relate to each other.
A perfect next step is learning how to convert decimals to percentages. This skill is incredibly direct. You can take a decimal like 0.75, multiply it by 100, and you've got 75%. These relationships are everywhere in the real world, from figuring out a sale price at a store to making sense of statistics in the news.
Struggling with a tricky math problem or need a step-by-step explanation for your homework? Feen AI is here to help. Get instant, clear solutions and chat-based support for Math, Physics, Chemistry, and more. Just upload a photo of your problem and get the guidance you need to succeed.
Recent articles
Discover what is dimensional analysis in chemistry and master the factor-label method with clear, step-by-step examples.
Master how to study for biology exam with proven methods: active recall, spaced repetition, and practice questions to boost mastery and scores.
Explore chemistry dimensional analysis practice with 8 problem types and step-by-step solutions covering unit conversions, stoichiometry, redox, and more.
Struggling with what is implicit differentiation? This guide uses simple analogies and clear examples to explain the concept, process, and common mistakes.
Struggling with what is momentum and impulse? This guide uses clear analogies and real-world examples to explain these core physics concepts simply.
Learn how to study for ACT Math with strategies that work. This guide covers smart prep, practice tests, and tips to raise your score.





