8 Types of Math Problems for 7th Graders (With Solutions)
Master key concepts with our detailed list of math problems for 7th graders. Includes examples, step-by-step solutions, and study tips for success.

7th grade is a pivotal year in mathematics, where abstract thinking begins to take center stage. Students move from concrete arithmetic to the foundational concepts of algebra, geometry, and statistics that pave the way for higher-level courses. This transition can be challenging, but mastering it is crucial for future academic success. This guide provides a comprehensive breakdown of essential math problems for 7th graders, designed to build both skills and confidence. We go beyond simple examples to offer a strategic problem-solving toolkit for students, parents, and educators alike.
This listicle is structured to provide deep, actionable insights. For each core topic, you will find:
- Tiered examples ranging from foundational to more complex applications.
- Step-by-step solutions that break down the "how" and "why" behind each calculation.
- Common pitfalls to help students recognize and avoid frequent errors.
- Actionable takeaways that reinforce key concepts and strategies.
Our goal is to demystify 7th-grade math, transforming potential roadblocks into launchpads for mathematical fluency. We will explore everything from two-step equations and percent word problems to the area of composite figures and simple probability. For students seeking personalized assistance, modern educational tools such as intelligent AI Tutors can offer on-demand support, explaining complex steps and reinforcing learning. By understanding the logic behind these problems, students can develop the critical thinking skills needed to excel in math and beyond. Let's dive into the core problems that define the 7th-grade curriculum.
1. Two-Step Equations with Integers
Two-step equations are a fundamental concept in 7th-grade math, acting as a crucial bridge between basic arithmetic and more complex algebra. These problems require you to perform two inverse operations to isolate a variable. Mastering them builds a strong foundation for solving nearly all future algebraic challenges, making them essential math problems for 7th graders.
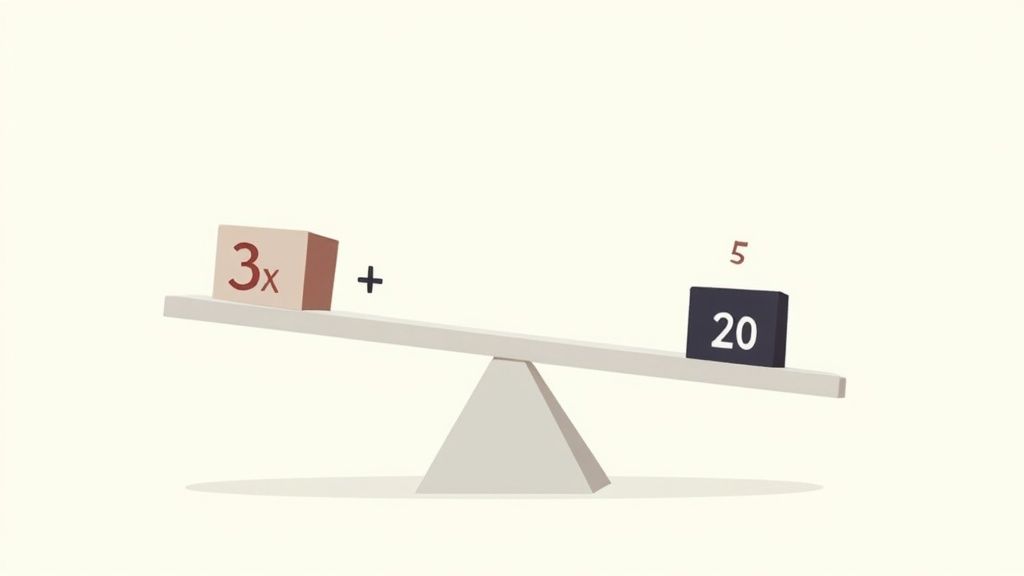
Think of an equation like a balanced scale. To keep it balanced, whatever you do to one side, you must also do to the other. The goal is to get the variable (like x) by itself on one side.
Why It's a Core Skill
This skill is not just about numbers; it's about logic and order. Solving a two-step equation teaches students to think backward and apply operations in a specific sequence, a strategy used in coding, scientific experiments, and financial planning. It’s the first real taste of procedural, multi-step problem-solving in algebra.
Example Problem and Solution
Let's solve a classic two-step equation: 4x - 7 = 13
Isolate the variable term: The first step is to undo the addition or subtraction. Here, we see "- 7", so we do the inverse operation: add 7 to both sides.
- 4x - 7 + 7 = 13 + 7
- 4x = 20
Solve for the variable: Now, undo the multiplication or division. The variable x is being multiplied by 4, so we divide both sides by 4.
- 4x / 4 = 20 / 4
- x = 5
Actionable Tips for Students
- Reverse PEMDAS: When solving, you undo the order of operations. Deal with addition/subtraction first, then multiplication/division.
- Check Your Work: Substitute your answer back into the original equation to verify it's correct. For our example: 4(5) - 7 = 20 - 7 = 13. It works!
- Watch for Negatives: Be extra careful when working with negative integers. Subtracting a negative is the same as adding a positive.
For a deeper dive into problem-solving frameworks, you can learn more about how to approach these challenges with our guide on how to solve math problems step-by-step.
2. Percent Word Problems
Percent word problems are a practical and essential type of math problem for 7th graders that connects abstract concepts to everyday life. These problems require students to calculate discounts, markups, tips, and changes, translating real-world scenarios into mathematical equations. Mastering percentages builds financial literacy and strengthens proportional reasoning skills.
These problems challenge students to identify the "part," the "whole," and the "percent" within a given story. The core idea is understanding that a percentage is simply a part of a whole, expressed as a fraction of 100. This application makes math feel relevant and immediately useful.
Why It's a Core Skill
This skill is crucial because it is one of the most frequently used math concepts in daily life. From calculating a 15% tip at a restaurant to understanding a 30% discount on a video game, percentages are everywhere. This topic develops critical thinking by forcing students to read carefully, identify key information, and determine what a question is truly asking, a skill vital for both academic and real-world success.
Example Problem and Solution
Let's solve a common percent word problem: A video game that originally costs $60 is on sale for 25% off. What is the final sale price?
Find the amount of the discount: First, calculate the value of the 25% discount. To do this, convert the percent to a decimal (25% = 0.25) and multiply it by the original price.
- Discount = 0.25 * $60
- Discount = $15
Calculate the final price: Now, subtract the discount amount from the original price to find the new sale price.
- Final Price = Original Price - Discount
- Final Price = $60 - $15
- Final Price = $45
Actionable Tips for Students
- Identify the "Whole": Before you start, always determine what the total or original amount is. This is the "whole" that the percentage is based on.
- Convert and Calculate: Convert the percentage to a decimal (divide by 100) or a fraction for easier multiplication.
- Use the Proportion Method: A reliable strategy is to set up a proportion: part / whole = percent / 100. Fill in the two values you know and solve for the missing one.
- Estimate Your Answer: Before solving, try to estimate. For example, 25% is 1/4, and 1/4 of $60 is $15. This helps you check if your final answer is reasonable.
3. Multi-Step Word Problems with Rational Numbers
Multi-step word problems involving rational numbers (fractions, decimals, and integers) represent a major step up in complexity. These problems require students to read a scenario, identify the necessary information, determine the correct sequence of operations, and execute calculations accurately. They are a true test of a student's number sense and logical reasoning, making them essential math problems for 7th graders.
Unlike single-step problems, these scenarios mirror real-world challenges where you rarely have all the information laid out in a simple equation. Students must act as detectives, piecing together clues and breaking a larger problem into a series of smaller, manageable tasks.
Why It's a Core Skill
This skill is fundamental to practical math application. Life's problems don't come in neat equations; they come as narratives. Calculating the cost of a home renovation project, planning a budget for a trip, or adjusting a recipe all involve multiple steps and a mix of rational numbers. Mastering these word problems builds critical thinking, resilience, and the ability to translate real-life situations into mathematical strategies.
Example Problem and Solution
Let's tackle a common scenario: A baker is making a cake. The recipe calls for 2.5 cups of flour. She wants to make a batch that is 1.5 times the original recipe. If she has a 5-cup bag of flour, how much flour will she have left after making the cake?
Find the total flour needed: First, determine how much flour the larger batch requires. You need to multiply the original amount by the scaling factor.
- 2.5 cups * 1.5 = 3.75 cups
- The baker needs 3.75 cups of flour for the cake.
Calculate the remaining amount: Now, subtract the amount of flour used from the total amount she started with.
- 5 cups - 3.75 cups = 1.25 cups
- The baker will have 1.25 cups of flour left.
Actionable Tips for Students
- Read and Reread: Read the problem at least twice. The first time, get the general idea. The second time, highlight or list the key numbers and what you need to find.
- Break It Down: Don't try to solve it all at once. Identify the first question you need to answer (e.g., "How much flour is needed?"), solve it, then move to the next.
- Watch Your Units: Make sure all your units are consistent. If a problem mixes feet and inches, convert them to the same unit before calculating.
- Check for Reasonableness: Does your answer make sense? If you get a negative amount of flour left, you know you made a mistake somewhere.
For a more detailed guide on structuring your approach, discover our strategies for how to solve word problems in algebra.
4. Geometry: Area and Perimeter of Composite Figures
Composite figures are shapes made up of two or more basic geometric shapes like rectangles, triangles, and circles. Solving for their area and perimeter requires students to break down complex problems into manageable parts. This skill is a cornerstone of 7th-grade geometry, pushing students to apply their knowledge of basic formulas in more creative and practical ways, making these essential math problems for 7th graders.
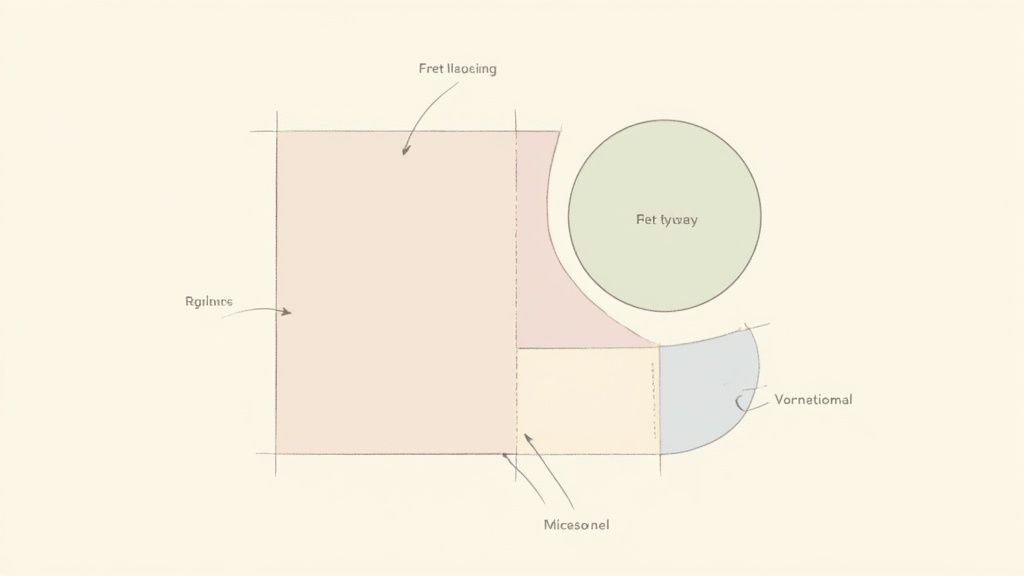
Think of it like building with blocks. You know the shape of each block (rectangle, triangle), and by putting them together, you can create a more complex structure. To find the total area, you just add up the areas of the individual blocks.
Why It's a Core Skill
This skill develops crucial spatial reasoning and problem-solving abilities. It teaches students to see the "parts" within a "whole," a valuable analytical skill used in fields like architecture, engineering, and even graphic design. Students learn to visualize, decompose, and reconstruct shapes, connecting abstract formulas to tangible, real-world applications like calculating the flooring needed for an L-shaped room.
Example Problem and Solution
Let's find the total area of a figure composed of a rectangle and a semicircle, where the rectangle is 10 cm long and 8 cm wide, and the semicircle is attached to one of the 8 cm sides.
Decompose the shape: Break the figure into its two components: a rectangle and a semicircle.
- Rectangle: Dimensions are 10 cm by 8 cm.
- Semicircle: Its diameter is the 8 cm side of the rectangle.
Calculate the area of each component:
- Area of rectangle = length × width = 10 cm × 8 cm = 80 cm².
- The radius of the semicircle is half the diameter, so r = 8 cm / 2 = 4 cm.
- Area of a full circle is πr². The area of a semicircle is (πr²) / 2.
- Area of semicircle ≈ (3.14 × 4²) / 2 = (3.14 × 16) / 2 = 50.24 / 2 = 25.12 cm².
Combine the areas: Add the area of the rectangle and the area of the semicircle.
- Total Area = 80 cm² + 25.12 cm²
- Total Area ≈ 105.12 cm²
Actionable Tips for Students
- Break It Down: The first step is always to divide the complex shape into familiar ones you know the formulas for.
- Find Missing Sides: Sometimes you'll need to use the given information to figure out the lengths of unmarked sides before you can calculate area or perimeter.
- Watch the Perimeter: When calculating the perimeter of a composite shape, remember to only add the lengths of the outer edges. Don't include the lines where the shapes connect.
5. Probability: Simple Event Problems
Probability introduces students to the mathematics of chance and likelihood, a concept with vast real-world applications. Simple event problems are a foundational element of this topic, teaching students how to calculate the chances of a single, specific outcome occurring. These math problems for 7th graders are essential for developing analytical and predictive thinking skills.
The basic formula for the probability of a simple event is the ratio of favorable outcomes to the total number of possible outcomes. This simple fraction forms the basis for understanding everything from weather forecasts to game strategies.

Why It's a Core Skill
Understanding probability is crucial for making informed decisions in everyday life. It helps students evaluate risks, understand statistics in the news, and grasp the fairness of games. This skill lays the groundwork for more advanced topics in statistics, data science, and even economics, making it a critical component of a 7th grader's mathematical education.
Example Problem and Solution
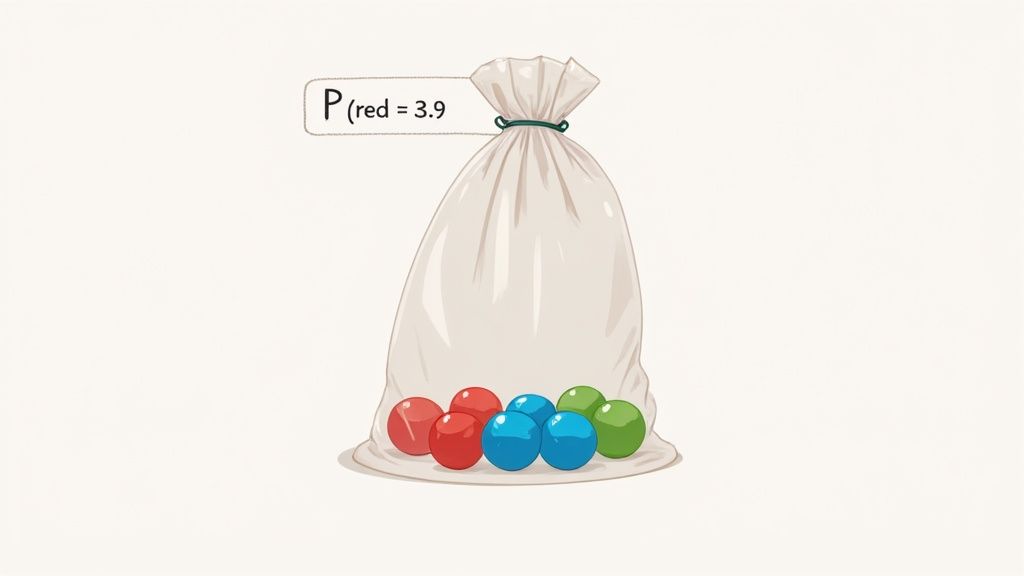
Let's calculate the probability of a simple event: In a bag with 3 red marbles, 4 blue marbles, and 2 green marbles, what is the probability of drawing a red marble?
Find the total number of possible outcomes: First, count all the marbles in the bag.
- 3 (red) + 4 (blue) + 2 (green) = 9 total marbles.
- This means there are 9 possible outcomes when you draw one marble.
Identify the number of favorable outcomes: The "favorable" outcome is drawing a red marble. There are 3 red marbles.
- Number of favorable outcomes = 3.
Calculate the probability: Now, write the ratio of favorable outcomes to total outcomes.
- Probability (Red) = (Number of Red Marbles) / (Total Number of Marbles)
- P(Red) = 3/9, which simplifies to 1/3.
Actionable Tips for Students
- List Systematically: Before calculating, always list or count all possible outcomes to find your denominator.
- Express It All Ways: Practice converting your probability between a fraction (1/3), a decimal (0.33), and a percentage (33.3%). This builds number sense.
- Remember the Range: Probability is always a value between 0 (impossible) and 1 (certain). If your answer is greater than 1, you've made a mistake.
6. System of Equations: Introduction Problems
While it may sound advanced, an introduction to systems of equations is a natural next step after mastering single-variable equations. These problems involve finding a single solution (an x and y value) that makes two different linear equations true at the same time. This concept is one of the most practical math problems for 7th graders, as it mirrors real-world scenarios where multiple conditions must be met simultaneously.
Think of it as finding the exact point where two straight paths cross. That single intersection point is the solution that lies on both paths. For 7th graders, this is typically explored by graphing the two lines and identifying where they meet.
Why It's a Core Skill
This skill introduces the powerful idea that problems can have multiple constraints. It’s the mathematical equivalent of decision-making, like finding the point where the cost of two different phone plans becomes equal. This builds a foundation for higher-level algebra, economics, and even computer programming, where systems must satisfy several conditions to function.
Example Problem and Solution
Let's find the solution for this system: y = 2x + 1 and y = -x + 4
Understand the Goal: We need to find the one coordinate pair (x, y) that exists on both lines. At this point, the 'y' from the first equation will be equal to the 'y' from the second equation.
Set the Equations Equal (Substitution Method): Since both equations are equal to y, we can set them equal to each other to solve for x.
- 2x + 1 = -x + 4
Solve for x: Now, we solve this like a regular multi-step equation. First, get the variable terms on one side by adding x to both sides.
- 3x + 1 = 4
- Subtract 1 from both sides: 3x = 3
- Divide by 3: x = 1
Solve for y: Substitute the value of x (which is 1) back into either of the original equations to find y. Let's use the first one.
- y = 2(1) + 1
- y = 2 + 1
- y = 3
The solution to the system is the coordinate point (1, 3).
Actionable Tips for Students
- Graph It Out: Use graph paper or an online tool to plot both lines. The point where they cross is your answer. This is a great way to visualize the solution.
- Check Your Work: Your solution must work in both original equations. Check (1, 3) in the second equation: 3 = -(1) + 4, which simplifies to 3 = 3. It works!
- Keep It Neat: Organization is key. Write down each step clearly to avoid mixing up numbers or signs.
Systems of equations are a gateway to more complex problem-solving. To build on these fundamentals, you can explore our detailed guide on how to solve systems of linear equations.
7. Integer Operations: All Four Operations with Negative Numbers
Mastering integer operations is one of the most significant leaps in 7th-grade math. These problems move beyond basic arithmetic by incorporating negative numbers into addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Fluency with integers is non-negotiable for success in algebra and beyond, as they appear in everything from solving equations to plotting points on a coordinate plane.
Understanding negative numbers can be tricky because it requires abstract thinking. Real-world scenarios like temperature dropping below zero, changes in bank account balances, or movement below sea level help make these concepts tangible. These are essential math problems for 7th graders because they build the numerical intuition needed for higher-level mathematics.
Why It's a Core Skill
This skill is the bedrock of algebra. Without a solid grasp of how to add, subtract, multiply, and divide with positive and negative numbers, students will struggle with solving equations, simplifying expressions, and understanding functions. It teaches precision and attention to detail, as a single misplaced negative sign can completely change the outcome of a problem.
Example Problem and Solution
Let's solve a multi-step problem involving all four operations: (-6) × 3 ÷ (-2) + 4
Follow the Order of Operations (PEMDAS/BODMAS): We handle multiplication and division first, from left to right. Start with (-6) × 3. A negative times a positive is a negative.
- (-6) × 3 = -18
- The problem is now: -18 ÷ (-2) + 4
Continue with Division: Next, we divide -18 by -2. A negative divided by a negative is a positive.
- -18 ÷ (-2) = 9
- The problem is now: 9 + 4
Perform the Final Addition: The last step is simple addition.
- 9 + 4 = 13
- The final answer is 13.
Actionable Tips for Students
- Visualize with a Number Line: Use a number line to model addition and subtraction. Adding a positive number moves you right, while adding a negative number (or subtracting a positive) moves you left.
- Create Rule Charts: Make a small chart for multiplication and division rules (e.g., "Same signs = positive," "Different signs = negative") and keep it handy while you practice.
- Context is Key: Think of money. If you have $10 and you subtract a debt of $5 (10 - (-5)), you are actually $15 richer. Using stories helps make the rules stick.
8. Proportional Relationships: Ratios and Scale Factor Problems
Proportional relationships are a cornerstone of 7th-grade math, teaching students how two quantities change together at a constant rate. These problems use ratios, rates, and scale factors to make sense of the world, from reading a map to scaling a recipe. Understanding proportionality is essential for grasping more advanced topics like slope, linear functions, and trigonometry.
Think of it as a consistent rule of comparison. If one apple costs $0.50, the "rule" or ratio is 1 apple to $0.50. This proportional rule allows you to determine the cost of any number of apples. These math problems for 7th graders build critical reasoning skills by applying this logic to real-world scenarios.
Why It's a Core Skill
Proportional reasoning is used everywhere. It's the logic behind architectural blueprints, cooking for a crowd, understanding fuel efficiency, and converting currency. Mastering these problems helps students develop a strong sense of number relationships and the ability to make logical predictions based on known information, a skill vital in science, engineering, and everyday decision-making.
Example Problem and Solution
Let's solve a common scale factor problem: A map has a scale of 1 inch : 50 miles. If the distance between two cities on the map is 3.5 inches, what is the actual distance between them?
Set up the proportion: The key is to create two equivalent ratios. We'll compare inches to miles. Let d represent the actual distance in miles.
- (1 inch / 50 miles) = (3.5 inches / d miles)
Solve for the unknown: We can use cross-multiplication to solve for d. This method involves multiplying the numerator of one fraction by the denominator of the other.
- 1 * d = 50 * 3.5
- d = 175
State the answer with units: The actual distance between the two cities is 175 miles.
Actionable Tips for Students
- Be Consistent: When setting up your proportion, make sure the units are in the same position on both sides (e.g., inches on top, miles on the bottom).
- Use Cross-Multiplication: For any proportion a/b = c/d, the cross-product is always true: a * d = b * c. This is a reliable way to solve for an unknown variable.
- Label Everything: Always write down the units (like inches, miles, cups, etc.). This helps prevent confusion and ensures your final answer makes sense in the context of the problem.
8-Point Comparison: 7th Grade Math Problems
| Topic | Implementation complexity | Resource requirements | Expected outcomes | Ideal use cases | Key advantages | Common challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two-Step Equations with Integers | Low–Moderate: simple inverse operations | Basic: worksheets, balance visuals, whiteboard | Variable isolation, procedural fluency in algebra | Intro algebra lessons, grade 6–7 practice | Clear step-by-step solutions; easily assessable | Sign errors, negatives confusion, order mistakes |
| Percent Word Problems | Moderate: context interpretation and conversions | Real-world contexts, calculators optional, word problem prompts | Proportional reasoning, financial literacy, percent fluency | Consumer math, discounts/tips, grade-level applied tasks | Highly relevant to daily life; multiple solution methods | Reading comprehension issues; increase vs. decrease confusion |
| Multi-Step Word Problems with Rational Numbers | High: multiple steps and number types | Scaffolding, manipulatives, real-world scenarios | Complex problem-solving, number sense, multi-step reasoning | Problem-based learning, real-world tasks (recipes, projects) | Integrates concepts; develops critical thinking | High cognitive load; error-prone multi-step processes |
| Geometry: Area and Perimeter of Composite Figures | Moderate–High: decomposition and combined formulas | Diagrams, graph paper, geometry software (GeoGebra) | Spatial reasoning; applying multiple area/perimeter formulas | Design tasks, architecture basics, geometry units | Visual learning; real-world application in design | Difficulty decomposing shapes; unit conversion errors |
| Probability: Simple Event Problems | Low–Moderate: counting and sample-space reasoning | Manipulatives, experiments, tree diagrams | Foundational probabilistic thinking; interpretation of likelihood | Introductory statistics, games, experiments | Engaging and concrete; supports experimental verification | Misunderstandings of independence; experimental vs theoretical gaps |
| System of Equations: Introduction Problems | Moderate: solving two linear equations (algebraic/graphical) | Graphing tools (Desmos), coordinate grids, algebra practice | Understanding constraints, intersection points, multiple methods | Intro to simultaneous equations, real-world comparisons | Connects algebraic and graphical viewpoints; method variety | Abstractness for some learners; graphing inaccuracies |
| Integer Operations: All Four Operations with Negative Numbers | Low–Moderate: procedural with sign rules and order of ops | Number lines, colored manipulatives, rule charts | Fluency with negatives; reliable arithmetic foundations | Foundational arithmetic, remediation, pre-algebra | Concrete models available; essential prerequisite skill | Counterintuitive sign rules; frequent calculation errors |
| Proportional Relationships: Ratios and Scale Factor Problems | Moderate: setting up and solving proportions | Ratio tables, double number lines, unit labels, diagrams | Proportional reasoning, scaling, unit conversion skills | Maps, scale models, recipes, speed/distance problems | Broad real-world applicability; visual strategies aid learning | Incorrect setup of proportions; unit and context confusion |
From Practice Problems to Lasting Proficiency
The journey through seventh-grade mathematics is a pivotal one, marking a significant transition from concrete arithmetic to more abstract and complex reasoning. The diverse array of math problems for 7th graders we've explored in this guide-from navigating two-step equations with integers to calculating the probability of simple events-are not just individual hurdles to overcome. They are interconnected building blocks that form the bedrock of all future mathematical studies, including algebra, geometry, and beyond.
True mastery isn't achieved by simply memorizing formulas or racing through problem sets. It's cultivated by developing a strategic, analytical mindset. By consistently engaging with these problems, you are training your brain to recognize patterns, deconstruct complex challenges into manageable parts, and apply logical reasoning-skills that are invaluable in every academic discipline and professional field.
Synthesizing Your Seventh-Grade Math Skills
As you reflect on the problems covered, from proportional relationships to the area of composite figures, several core strategies emerge as universally effective. These are the meta-skills that separate fleeting knowledge from deep, lasting comprehension.
- Deconstruction is Key: The most intimidating multi-step word problems become approachable when you break them down. Your first step should always be to identify the knowns, the unknowns, and the ultimate question being asked. This systematic approach turns a wall of text into a clear, actionable plan.
- Visualize the Concept: Whether it's sketching a composite geometric shape, drawing a number line for integer operations, or using a bar model for percent problems, visualization is a powerful tool. It transforms abstract numbers and variables into tangible concepts, often revealing the path to a solution that wasn't immediately obvious.
- Embrace the "Why": Don't just follow the steps; understand the logic behind them. Why does isolating the variable work in an equation? Why does the formula for the area of a circle involve pi? Asking "why" deepens your understanding and makes the knowledge stick, allowing you to adapt your skills to new and unfamiliar problems.
Actionable Next Steps for Continued Growth
Proficiency is a continuous process, not a final destination. To build on the foundation you've established, it's crucial to adopt habits that reinforce learning and build unshakable confidence. Here are your next steps:
- Consistent, Varied Practice: Dedicate regular, focused time to practice. Don't just stick to one type of problem; mix it up. Work on geometry one day and ratios the next. This "interleaved" practice strengthens your ability to recall and apply the correct strategy for any given challenge.
- Analyze Your Mistakes: An incorrect answer is not a failure; it's a valuable learning opportunity. When you get a problem wrong, don't just look at the right answer and move on. Meticulously review your work to pinpoint exactly where the error occurred. Was it a simple calculation mistake, a conceptual misunderstanding, or a misread of the question?
- Articulate Your Process: Try explaining how to solve a problem out loud to a friend, a parent, or even just to yourself. This act of verbalizing your thought process, known as the "Protégé Effect," forces you to clarify your understanding and solidifies the concepts in your mind.
The ultimate goal of working through these math problems for 7th graders is to develop mathematical fluency and confidence. It's about building a toolkit that empowers you to approach any quantitative challenge with a sense of curiosity and a belief in your ability to find a solution. This skill set will serve you well, unlocking doors to advanced STEM courses and equipping you with the critical thinking abilities needed to navigate an increasingly data-driven world.
When you're stuck on a tricky homework problem or need a clearer explanation of a core concept, Feen AI is ready to help. Simply upload a picture of any of the math problems for 7th graders you're working on, and get instant, step-by-step guidance that not only shows you the answer but explains the "why" behind it. Transform your study sessions and build lasting math confidence with your personal AI tutor at Feen AI.
Relevant articles
Struggling with algebra or geometry? This guide breaks down key math problems for 9th graders with examples, solutions, and pro tips to help you succeed.
Struggling with middle school math? Master key concepts with our huge list of math problems for 8th graders, complete with answers, worksheets, and tips.
Master core concepts with these essential math problems for 6th graders. Includes free worksheets, solutions, and tips to build confidence and skills.
Discover key math problems for 5th graders covering fractions, geometry & more. Includes step-by-step solutions & teaching tips to boost skills.
Discover the best platforms with quality math problems for 3rd graders. Find free worksheets, online games, and challenging problem sets to boost skills.
Discover our comprehensive roundup of math problems for 2nd graders, with free practice sets for addition, word problems, money, and more to boost skills.





