Your Ultimate Organic Chemistry Study Guide for Success
Struggling with O-Chem? Our complete organic chemistry study guide covers mechanisms, spectroscopy, and study strategies to help you master the course.

Your best organic chemistry study guide isn't about memorizing facts—it's a roadmap built on active learning, consistent practice, and pattern recognition. This mindset shifts the subject from a terrifying list of reactions into a logical puzzle, making even the most complex ideas feel manageable.
Why Organic Chemistry Feels So Hard (and How to Fix It)
Let's get one thing straight: organic chemistry is tough. If you're finding it difficult, you’re not alone. The feeling of being completely overwhelmed is a universal experience for students tackling this subject.
This isn't just a feeling; the numbers back it up. In one study of high school and university students, a staggering 59.8% said they found the subject difficult, and their median diagnostic test score was a sobering 52%. You can dig deeper into these student perceptions in this detailed research paper.
The key to getting past this wall isn't about studying harder—it's about studying smarter. It all starts with a change in perspective. Instead of treating O-Chem like a history class full of dates and names to memorize, think of it as learning a new language.
Learning the Language of Molecules
Organic chemistry truly has its own language, complete with an alphabet, vocabulary, and grammar.
- The Alphabet: These are your atoms—Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and a few others. They're the basic letters you'll use to build everything.
- The Vocabulary: These are the molecules and functional groups. Think of them as the words you form by combining the atomic "letters" in specific ways.
- The Grammar: These are the reaction mechanisms and core principles that explain why and how molecules interact. This is the set of rules that governs everything.
You can’t write a meaningful sentence by just throwing random words on a page. Likewise, you can't solve a reaction problem by just memorizing what the starting material and final product look like. You have to understand the "grammar"—the rules of how electrons move—that drives the entire process.
From Memorization to Pattern Recognition
The single biggest mistake students make is trying to brute-force memorize every reaction. It’s an exhausting and doomed strategy. There are simply too many.
A much better approach is to focus on understanding the fundamental patterns. Once you grasp the core principles, you'll start to see that hundreds of different reactions are really just slight variations of a few key themes.
This guide is designed to be your roadmap. We won't just list facts. We will show you how to build your knowledge from the ground up, starting with the foundational "grammar" and moving toward a deep understanding of complex problems.
Before we dive in, here's a high-level look at the core pillars of our approach. Each one is a crucial skill you'll need to develop to truly master the subject.
Your Roadmap to Mastering Organic Chemistry
| Study Pillar | Key Skill to Develop | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Conceptual Foundation | Understanding why things happen, not just what happens. | This builds the intuition needed to predict reaction outcomes instead of just memorizing them. |
| Reaction Mechanisms | Visualizing electron movement with arrow-pushing. | This is the "grammar" of O-Chem. Master this, and you can solve almost any problem. |
| Problem-Solving | Applying concepts to unfamiliar problems. | Exams won't give you problems you've seen before. You need the skill to tackle new challenges. |
| Spaced Repetition | Consistently reviewing material over time. | This moves information from short-term to long-term memory, which is essential for a cumulative subject. |
By focusing on these areas, you'll build a solid, interconnected web of knowledge that you can rely on.
The goal isn't just to survive organic chemistry; it's to understand its inherent logic. When you focus on the 'why' behind each reaction, you're building a problem-solving toolkit that will serve you long after the final exam.
By following this structured plan and using modern tools like Feen AI to get instant feedback and clarification, you can turn this intimidating course into an achievable—and even enjoyable—challenge. Let's get started.
Building a Strong Foundation with Core Concepts
If you jump into organic chemistry without a firm grasp of the basics, you're setting yourself up for a struggle. It’s like trying to build a house on a foundation of sand. Everything that comes later—the complex reactions, stereochemistry, and spectroscopy—all hinges on a handful of core ideas. This part of the guide is all about building that solid foundation.
The real secret here is to stop memorizing abstract rules. Instead, you need to develop an intuition for why molecules behave the way they do. We'll use some clear analogies to make these concepts stick, turning them from dry textbook jargon into tools you can actually use to predict chemical behavior.
Visualizing the World of Atoms and Electrons
Everything in organic chemistry starts with atoms and their electrons. For a moment, let's forget the dense definitions of orbitals and think of them as "neighborhoods" where electrons are most likely to hang out. An s-orbital is like a simple, spherical studio apartment. P-orbitals are more like dumbbell-shaped two-room suites, each pointing down a different axis (x, y, and z).
Now, atoms don't just keep these orbitals separate. They often mix and match them to form better, stronger bonds. This process, called hybridization, is like an atom renovating its available apartments to create new, specialized spaces that allow for stronger connections with its neighbors.
- sp³ Hybridization: Here, an atom blends one s-orbital and three p-orbitals to create four identical, perfectly spaced hybrid orbitals. Think of methane (CH₄), where the carbon atom forms four single bonds that point to the corners of a tetrahedron.
- sp² Hybridization: An atom mixes one s-orbital with two p-orbitals, leaving one p-orbital completely untouched. This gives you three hybrid orbitals that lie flat in a single plane, which is the key to forming double bonds.
- sp Hybridization: In this case, an atom combines one s-orbital and one p-orbital, leaving two p-orbitals free. The resulting linear arrangement is what allows for triple bonds.
Understanding hybridization isn't just academic trivia; it’s a powerful tool that directly predicts a molecule's shape and, by extension, its reactivity.
The three-dimensional shape of a molecule, dictated by its bonding and electron pairs, is one of the most important factors in determining its physical and chemical properties. Mastering these foundational concepts makes the rest of the subject feel logical rather than random.
Understanding How Molecules Take Shape
Once atoms have their hybridized orbitals ready, they form bonds. The two most important types you'll encounter are sigma (σ) and pi (π) bonds.
A sigma bond is the first, and strongest, connection between two atoms. It’s formed by the direct, head-on overlap of orbitals. Think of it as a firm handshake. Every single, double, and triple bond has exactly one sigma bond holding it together.
Pi bonds, on the other hand, are formed from the sideways overlap of those unhybridized p-orbitals we mentioned earlier. They're weaker than sigma bonds and only show up in double bonds (which have one σ and one π bond) and triple bonds (one σ and two π bonds). The presence of pi bonds almost always makes a molecule more reactive because their electrons are more exposed and easier for other molecules to access.
To figure out the final 3D geometry, we use a concept called VSEPR Theory (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion). The idea behind it is surprisingly simple: electron pairs, whether they're in bonds or just sitting as lone pairs, repel each other. They will naturally arrange themselves to be as far apart as possible. This one simple rule explains why methane is tetrahedral and why a water molecule is bent. While this idea comes from general chemistry, knowing how to balance chemical equations and account for every atom and electron is a critical skill that carries right over.
Functional Groups: The Personalities of Molecules
With a handle on structure and bonding, we can finally talk about functional groups. The best way to think of these is as the "personality types" of the molecular world. A functional group is just a specific arrangement of atoms inside a larger molecule that gives the molecule its characteristic chemical behavior.
Just like you can predict how a person might act based on their personality, you can predict how a molecule will react once you identify its functional group.
- An alcohol (-OH group) is going to behave in a very different way than a carboxylic acid (-COOH group).
- An alkene (C=C double bond) has a completely different reactivity profile than an alkane (which only has C-C single bonds).
Learning to spot these groups instantly is non-negotiable. They are the essential vocabulary of organic chemistry. Once you master this foundational language of atoms, bonds, shapes, and functional groups, you’ve set the stage to understand the complex "conversations"—the reactions—that make up the heart of this subject.
Decoding the Logic of Reaction Mechanisms
Once you've got a handle on what molecules look like standing still, it's time to get them moving. Reaction mechanisms are the absolute heart of organic chemistry. They show the step-by-step story of how chemicals actually transform. Trust me, trying to memorize hundreds of individual reactions is a recipe for disaster. The real secret is understanding the why—the underlying mechanism that lets you predict the outcome of reactions you've never even seen before.
Think of it like choreographing a dance where the electrons are the dancers. Our job is to follow their every move. The language we use for this is called curved arrow notation. Each arrow shows a pair of electrons moving from a place where they're plentiful (a nucleophile) to a place where they're wanted (an electrophile). If you can master pushing these arrows around, you've mastered the single most important skill in the entire course.
This is why we spent time on structure and bonding first. You can't understand the dance until you know the dancers.
As you can see, it's a clear progression. You have to master the basics of structure before you can truly grasp how functional groups will behave when a reaction kicks off.
Key Substitution and Elimination Reactions
In your first organic chemistry course, you'll spend a ton of time on a handful of core reaction types. Substitution and elimination reactions are the perfect battleground to see how different mechanisms compete. You'll learn how tiny tweaks to the reaction conditions can lead to completely different products.
Let’s quickly break down the four big ones: SN1, SN2, E1, and E2.
- SN2 (Substitution Nucleophilic Bimolecular): Picture a perfectly timed, one-step maneuver. A nucleophile attacks a carbon atom and kicks out the "leaving group" all in one fluid motion. For this to work, the nucleophile needs a clear path to attack from behind, which means it’s very sensitive to bulky groups getting in the way (we call this steric hindrance).
- SN1 (Substitution Nucleophilic Unimolecular): This one is a two-step dance. First, the leaving group just leaves on its own, creating a positively charged intermediate called a carbocation. Then, in the second step, the nucleophile comes in and attacks this carbocation.
- E2 (Elimination Bimolecular): Like the SN2, this is a concerted, one-step process. A strong base comes in and rips a proton off a carbon next to the one with the leaving group. This triggers a domino effect, forming a double bond and ejecting the leaving group simultaneously.
- E1 (Elimination Unimolecular): This reaction mirrors the SN1. It starts with the same first step: the leaving group departs, forming a carbocation. But instead of being attacked by a nucleophile, a weak base plucks off a nearby proton to create a double bond.
Getting a feel for the difference between stable intermediates (like carbocations) and fleeting transition states (the peak energy point of any given step) is absolutely essential for predicting which pathway a reaction will actually take.
The most powerful skill you can develop in organic chemistry is not memorization, but the ability to look at a set of reactants and conditions, and logically deduce the most probable mechanism. This turns a guessing game into a systematic process of elimination.
Why Stereochemistry Is a Matter of Life and Death
As you start tracing these reaction pathways, you'll quickly discover that the 3D arrangement of atoms—what we call stereochemistry—is a huge deal. This isn't just some abstract topic for the textbook; it has profound, real-world consequences.
The tragic story of thalidomide is the ultimate case study. Back in the 1950s and 60s, this drug was given to pregnant women for morning sickness. The problem is, the thalidomide molecule exists as two enantiomers—they're non-superimposable mirror images of each other, just like your left and right hands.
One enantiomer, (R)-thalidomide, was a safe and effective sedative. Its mirror image, (S)-thalidomide, was a teratogen, a compound that causes catastrophic birth defects. The drug was sold as a mix of both, and as a result, thousands of children were born with life-altering deformities. This medical disaster drove home a critical lesson: understanding a molecule's precise 3D shape is not optional. It can literally be a matter of life and death.
When you study a mechanism like SN2, you'll learn that the reaction proceeds with an "inversion of configuration," flipping the product's 3D arrangement like an umbrella caught in a strong wind. SN1 reactions, on the other hand, often create a mixture of stereoisomers because the flat carbocation intermediate can be attacked from either side with equal ease.
This is the whole point of an organic chemistry study guide like this one. It's about getting you past rote memorization and giving you the tools to predict how a reaction will happen, right down to its specific 3D structure. When you learn to "follow the electrons," you gain a deep, predictive power that transforms this subject from a scary list of facts into a beautiful, logical science.
Using Spectroscopy to See Molecular Structures
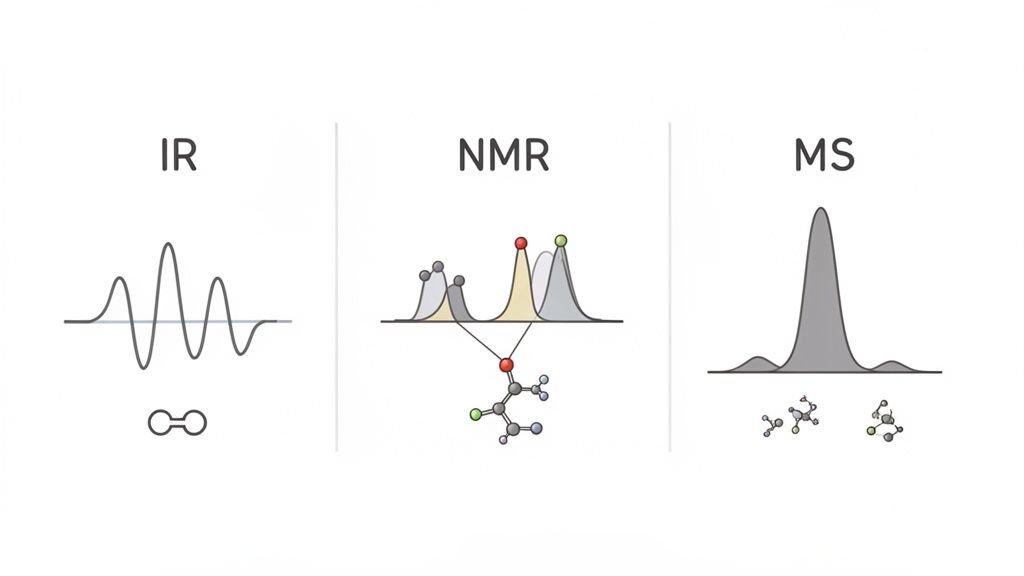
Once you get a handle on how molecules react, the next big challenge is figuring out how to identify them. Molecules are way too small to see, so chemists have developed a powerful toolkit of analytical techniques called spectroscopy. The best way to think about it is that you're "interviewing" the molecule, with each method asking different questions to reveal its structure.
Mastering spectroscopy isn't about rote memorization. It’s about becoming a molecular detective. You'll get a stack of clues—graphs with peaks, signals, and fragments—and your job is to piece everything together to solve the puzzle. This skill is a cornerstone of every good organic chemistry course.
Reading Vibrational Fingerprints with IR Spectroscopy
Picture every chemical bond as a tiny, invisible spring. These springs are always in motion, stretching and bending at very specific frequencies. Infrared (IR) spectroscopy works by zapping a sample with infrared light and seeing which frequencies get absorbed by these vibrating bonds.
This absorption pattern creates a unique "vibrational fingerprint" for every molecule. The real magic is that certain functional groups always show up as predictable peaks on the IR spectrum, giving you immediate clues.
- A big, broad, U-shaped peak hanging out around 3300 cm⁻¹ is the classic giveaway for an O-H bond from an alcohol. You can't miss it.
- See a sharp, intense peak right around 1700 cm⁻¹? That’s almost certainly a C=O (carbonyl) bond, the signature of ketones, aldehydes, and their relatives.
- Sometimes, what isn't there is just as important. No major peaks in those key regions helps you confidently rule out entire classes of compounds.
By spotting these key peaks, you can quickly get a read on the functional groups present in an unknown molecule. It's your first big break in the case.
Mapping the Atomic Social Network with NMR Spectroscopy
While IR is great for identifying functional groups, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy provides a detailed map of the carbon-hydrogen framework itself. It’s like building a social network profile for the molecule, showing you which atoms are connected and what their neighbors are like.
¹H NMR, which focuses on the hydrogen atoms, is packed with information. A single spectrum gives you four critical pieces of data:
- Number of Signals: This tells you how many unique "types" of protons exist in the molecule.
- Chemical Shift (Position): Where a signal appears on the graph points to the proton's electronic environment. A proton near an oxygen, for instance, will be shifted further "downfield."
- Integration (Area): The area under each signal reveals the ratio of protons of each type.
- Splitting Pattern (Multiplicity): This is the goldmine. The pattern tells you how many protons are on the adjacent carbons, allowing you to piece the structure together.
Honestly, NMR is probably the most powerful tool we have for figuring out a structure. The ability to see the exact connectivity between atoms turns what seems like an impossible puzzle into a solvable logic problem.
Weighing the Pieces with Mass Spectrometry
Last but not least, Mass Spectrometry (MS) gives us one more crucial data point: the molecule's weight. Unlike the other two techniques, MS is destructive. It basically smashes the molecule into pieces and then weighs those fragments by measuring their mass-to-charge ratio.
The heaviest fragment you see is usually the molecular ion peak (M⁺), which corresponds to the molar mass of the whole compound. This is incredibly useful. If you know the molecular formula is C₅H₁₀O, for example, you can quickly calculate if the molecule contains any rings or double bonds. The smaller peaks in the spectrum represent the broken pieces, offering even more clues about how the molecule is built.
By combining the intel from all three—IR for functional groups, NMR for the C-H framework, and MS for the molecular weight—you can systematically put all the pieces together and identify an unknown compound with confidence.
Creating a Study Plan That Actually Works
Let's be honest: you can't conquer organic chemistry by pulling an all-nighter before the midterm. It just doesn't work that way. Success in this course is built through consistent, focused effort—not through sheer willpower and caffeine. The best study guide is the one you build for yourself, centered around active engagement rather than just passively staring at your notes.
The big shift you need to make is from being a passive student to an active learner. That means getting your hands dirty and forcing your brain to do the heavy lifting, connecting the dots and building real, lasting knowledge.
Embrace Active Learning Over Passive Review
We've all been there—re-reading the textbook for the third time, highlighting every other sentence, or zoning out while re-watching a lecture. These activities feel productive, but they often create an illusion of understanding. True learning happens when you force yourself to retrieve and apply information. This is active learning.
And this isn't just a hunch; the data backs it up. A massive decade-long study involving 9,254 students showed that active-learning strategies led to incredible results. For underrepresented minority students, withdrawal and failure rates plummeted by almost 49%. That’s the kind of impact that engaged, hands-on learning can have.
So, how do you put this into practice? Here are a few non-negotiable strategies for your study plan:
- Draw, Don't Just Read: Never, ever just look at a reaction mechanism. Get out a blank sheet of paper and draw it from memory. Push the electrons yourself. This is how you build the instinct for how molecules behave.
- Build with Models: Get a molecular model kit. Seriously. Trying to visualize complex 3D concepts like stereochemistry or chair conformations on a flat page is incredibly difficult. Holding the molecule in your hands makes it click almost instantly.
- Solve Problems First: Before you even glance at the solutions manual, wrestle with the practice problems. The struggle is the most important part of the process. Getting stuck isn't a failure; it’s a signpost showing you exactly what you need to work on.
The most valuable part of studying is the moment you get stuck on a problem and have to fight your way to the solution. Resisting the urge to immediately check the answer key is how you build true problem-solving strength.
Structuring Your Study Week
A solid study plan needs to balance learning new material with constantly reviewing the old. Just reading the textbook cover-to-cover is one of the least effective ways to learn; for a better approach, check out our guide on how to study a textbook effectively. Instead, your schedule should be built around active, hands-on tasks.
To get the most out of your time, it’s also important to use effective strategies on how to focus while studying and make every session count.
Here’s a sample weekly schedule you can steal and adapt. The goal is to create a rhythm of learning, practicing, and reviewing.
Sample Weekly Organic Chemistry Study Schedule
This template helps you structure your week to balance absorbing new information from lectures with the active practice and review needed to actually master it.
| Day | Monday-Wednesday | Thursday-Friday | Saturday-Sunday |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | New Concepts & Initial Practice | Deep Practice & Clarification | Consolidation & Review |
| Tasks | Attend lecture. Pre-read the next chapter. Work through "end of chapter" problems related to the new topics. | Redo difficult problems. Form a study group to work through mechanisms on a whiteboard. Use office hours. | Review notes from the entire week. Create flashcards for new reactions. Take a practice quiz on all topics covered so far. |
This schedule keeps you from falling behind and transforms studying from a massive chore into a manageable, daily habit.
When you inevitably hit a wall on a tough problem, don't let it derail your entire study session. This is where modern tools can be a lifesaver. If a homework problem has you stumped, an AI tutor like Feen AI can walk you through it step-by-step. The goal isn't just to get the answer, but to understand the why behind it. This way, you can get unstuck quickly and keep your momentum going.
Essential Tools and Resources for O-Chem Students
Let's be real: tackling organic chemistry is a huge undertaking, but you absolutely don't have to go it alone. Having the right tools in your corner can be the difference between frustrating all-nighters and productive, confidence-building study sessions.
Think of your textbook as your foundational reference, but don't stop there. Supplement it with resources built specifically to help students connect the dots. A classic for a reason is David Klein’s Organic Chemistry as a Second Language. It’s fantastic at breaking down intimidating topics into smaller, more manageable pieces. If you're more of a visual learner, the step-by-step video tutorials on Khan Academy are a lifesaver, and Chem LibreTexts offers a massive open-source digital library packed with examples.
Your 24/7 Digital Tutor
This is where modern study tools can really give you an edge. An AI-powered helper acts like a personal tutor that’s available anytime you get stuck, helping you get unstuck fast and keep your momentum going.
Here’s how you can make an AI tool work for you:
- Homework Help: Hitting a wall with a problem set? Instead of spinning your wheels, just snap a picture and upload it. You’ll get a full, step-by-step solution that explains the why behind the answer, not just the what.
- Concept Clarification: If resonance or stereochemistry just isn't clicking after a lecture, you can ask for a simpler explanation or even a helpful analogy to make the concept stick.
- Practice Problem Generation: Getting ready for an exam and need to drill SN1/SN2 reactions? Ask the AI to whip up a few custom problems so you can get the reps you need.
And don't forget to take care of yourself during those long study marathons. Staring at screens and textbooks for hours can take a toll. To keep your focus sharp and reduce fatigue, it's worth looking into helpful tools like glasses for eye strain.
A quick note on using an AI solver: this is all about working smarter. The idea isn't to get the answers, but to use it as an on-demand tutor to truly understand the process. When you see the logic broken down, you reinforce your own learning and build the skills to solve similar problems on your own come exam time. You can learn more about how to effectively use a chemistry AI solver on our blog.
Answering Your Toughest Organic Chemistry Questions
Even with the best roadmap, you're bound to hit a few roadblocks. Let's tackle some of the most common questions and sticking points that trip students up.
Think of this as your personal Q&A session for those nagging problems that keep you from feeling confident before an exam.
How Much Time Should I Actually Study Each Week?
A good starting point is to budget 2-3 hours of study time for every hour you spend in lecture. So, if you have three hours of class per week, you're looking at about 6-9 hours of dedicated study.
But here's the real key: it's not about the hours you clock in, but what you do with that time. Active learning is everything. Instead of just re-reading your notes, you should be actively working problems, drawing mechanisms from scratch, and even trying to explain concepts out loud. Spreading these sessions out across the week is also far more effective than a marathon cram session.
Memorization is a fragile strategy in organic chemistry; it falls apart the moment you see a problem that looks slightly different. Understanding the 'why' behind a reaction—the mechanism—is what allows you to solve problems you've never seen before.
Should I Just Memorize the Reactions or Learn the Mechanisms?
Focus on the mechanisms. Always. Trying to memorize every single reaction is a recipe for disaster. It's like memorizing the answer to a single math problem instead of learning how to do algebra.
Yes, you'll need to remember some reagents and reaction names, but the real power comes from understanding the predictable patterns of how electrons move. Once you grasp the mechanisms, you'll have the tools to solve countless new problems because you'll see they all follow the same fundamental principles.
What's the Single Most Important Skill I Need to Master?
Without a doubt, it's "electron pushing" with curved arrows. This is the language of organic chemistry. Everything boils down to showing how electrons move from a place where they are plentiful (a nucleophile) to a place where they are wanted (an electrophile).
If you can master this one skill, you've unlocked the entire course. Practice it every single day. It turns what looks like a random collection of reactions into a logical, step-by-step story that you can actually follow and predict.
How Can I Use an AI Tool Without It Feeling Like Cheating?
The trick is to use it as a 24/7 personal tutor, not an answer generator. When you're stuck on a problem, give it a real, honest try first. Then, you can turn to an AI tool to ask for a specific hint or to check your final work.
The goal isn't just to get the answer, but to use the step-by-step explanation to find the exact point where you went wrong. You can also ask it to explain a concept from your lecture in a totally new way or create extra practice problems for a topic you’re struggling with. When you use it like that, it’s a powerful way to accelerate your learning, not just skip it.
Hitting a wall with a tough problem set or a confusing mechanism? Let Feen AI be your personal tutor. Just upload a photo of your question and get a clear, step-by-step explanation in seconds. It's the perfect way to get unstuck and truly master the concepts. Give it a try at https://feen.ai.
Recent articles
Struggling with circuit homework? Learn the rules of voltage drop in a parallel circuit with simple analogies, clear formulas, and solved examples.
Learn how to solve optimization problems in calculus with our definitive guide. Master the techniques to find maximum and minimum values using real examples.
Learn how to write a strong argumentative essay with our guide. We cover building a thesis, using evidence, and structuring your argument for academic success.
Discover how to prepare for organic chemistry using proven strategies. Our guide breaks down the essential study methods and tools you need to succeed in Orgo.
Struggling with statistics? Learn how to solve probability problems using core concepts, proven techniques, and real-world examples in this practical guide.
Unlock the best way to study for finals with 10 evidence-based strategies. Our guide covers everything from active recall to using Feen AI for success.





